What are nanobubbles (ultrafine bubbles)?
Ultrafine bubbles literally mean extremely small bubbles.
Exactly what size of bubbles can be referred to as ultrafine bubbles is yet to have been formally determined by The Japanese Society for Multiphase Flow.
However, with respect to their physical size, they should be smaller than approximately 50 microns.
Bubbles with a smaller diameter than 50 microns get compressed by ions at the gas-liquid interface.
This results in the ion concentration at the gas-liquid interface increasing, and both the internal pressure and temperature rising,
which then leads to various types of phenomena.
We are attempting to develop the potential of nanobubbles using the various types of phenomena.
History of ultrafine bubbles
Surprisingly enough, ultrafine bubbles actually have a long history. In 1894, when the Royal Navy was testing a high-speed torpedo boat for the first time they discovered that a violently vibrating torpedo boat propeller got significantly corroded on its surface. They observed that the rotating propeller generated a lot of bubbles and that its surface actually got covered in those bubbles. They therefore explored the hypothesis that the generation and extinguishment of the bubbles may actually be the cause of the corrosion of the propeller. Use of a larger propeller or a slower rotation speed moderated the cavitation problem. However, they had reached a dilemma in that even though a high-speed torpedo boat must be very fast, increasing its speed could be a fatal blow to it. The Royal Navy then requested Lord Rayleigh (whose birth name was John William Strutt), a legendary figure in classical physics, to investigate possible answers. He discovered that the microbubbles generated collapsing on the surface of the propeller resulted in a violent turbulent flow, and high levels of heat and pressure. He then developed a model (Rayleigh-Plesset Eq.) that provided the following values: 10,000 degrees Celsius and 10,000 atmospheres. Scientific research that originates out of a specific need is typically very practical. The above investigation also revealed that the noise of hot water in kettles directly before boiling point is reached results from ultrasound generated by microbubbles.

Six ultrafine bubble generation methods
1. Swirl-type liquid flow method
2. High pressure dissolution method
3. Ejector method
4. Venturi method
5. Mixed vapor direct contact condensation method
6. Supersonic vibration method

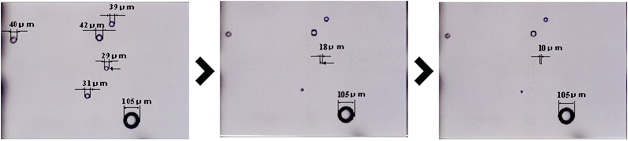
How to Generate Ultra Fine Bubbles
There are six typical methods for generating Fine Bubbles:
(1) By Swirl Flow
A liquid is injected at high speed into a cylinder from the tangential direction to produce a swirl flow in the cylinder so that the liquid issues in a jet from the hole at the center of the top end. At this time, the liquid pressure around the swirl axis decreases by an amount corresponding to the dynamic pressure, which allows the gas to be sucked through the hole of the bottom end. The sucked gas is transformed into the Ultra Fine Bubbles when passing through the hole of the top end.

(2) By Pressure Dissolution
Air is dissolved into water under pressure so that the water is supersaturated with the dissolved gas. The pressure of the water is rapidly injected through a pressure regulator. The dissolved gas is then released as the Ultra Fine Bubbles from the water until the supersaturation disappears. This phenomenon takes place on the same principle as bubbles rising from beer.

(3) By Ejector
The flow channel is deformed so that cavitations and therefore the Ultra Fine Bubbles occur in the gas distributor.

(4) By Venturi Tube
Both the gas and liquid are fed simultaneously into a venturi tube having a constricted section named “straw” in the flow channel, with the result that a rapid change in liquid flow rate yields a shock wave which crushes gas bubbles into the Ultra Fine Bubbles.

(5) By Mixed Vapor Condensation by Direct Contact with Coolant Water
Mixed vapor consisting of steam and a non-condensable gas is dispersed as vapor bubbles from a nozzle into coolant water. Steam in the vapor bubbles is cooled and condensed to water, which extremely reduces the volume of the bubbles. The presence of the non-condensable gas, however, hinders full condensation, thus generating the Ultra Fine Bubbles.

(6) By Ultrasonic Vibrations
The liquid is subjected to ultrasonic vibrations so that cavitations occur in the liquid, resulting in the Ultra Fine Bubbles being generated.
(7) By Nanopores
The gas is ejected through nano-scale pores while the liquid is being fed to the pore interface, which minutely cuts the gas phase into the Ultra Fine Bubbles.

Comparison of Various Fine Bubble Systems
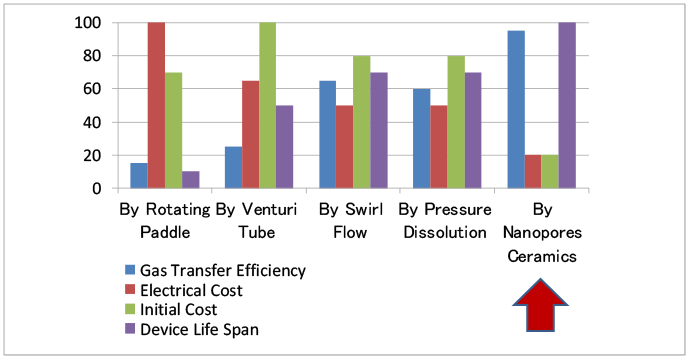
- Gas Transfer Efficiency: Shows how much input gas remains in the liquid. *Rotary Water Turbine – evaluation only.
- Electricity Cost: Comparison with oxygen supply ability per 1kw. The cost includes all electric power such as water pump, compressor etc.
- Initial Cost: Based on assuming the required oxygen is the same amount for all systems.
- Equipment Life Span: Comparison including pumps and motors.
The Method of Generating Ultra Fine Bubbles and Each of its Features
| I | 1. By Swirl Flow 2. By Ejector 3. By Venturi |
Mechanically shreds large bubbles into smaller bubbles High pressure is required for water flow The system cannot be used for high viscous or liquid containing large amounts of foreign matter |
Pros Self air supply is possible Installation is easy with the other device Cons Difficult to scale up Gas transfer efficiency is less than 65% High pressure pump is required Not suitable for high viscosity liquid Not suitable for liquid containing foreign matter Not suitable for concatenation or circulation pumps |
| II | 4. By Pressure Dissolution 5. By Ultrasonic Vibration |
Precipitating pre-dissolved gas content from the liquid as bubbles Both high pressure water and gas are required for pressurized dissolution method.Ultrasonic generator is required for ultrasonic method | Pros Medium-sized equipment is possible Many user track record Cons Gas transfer efficiency is less than 65% High pressure pump required Not suitable for liquid (20C/ 68F or higher) Ultrasonic type is expensive |
| Ⅲ | 6. By Mixed Vapor Condensation by Direct Contact with Coolant Water | Gas mixed into saturated steam and blown into the liquid to generate fine bubbles | Pros Large scale equipment is possible Cons Application scope is limited Temperature restriction |
| Ⅳ | 7. Nano pores | A method of generating ultrafine bubbles directly in liquid from ultra fine pores such as ceramics | Pros Flexibility in size from a small scale to a large scale Suitable for all type of liquids, gases and temperatures High gas transfer efficiency of (90%) Low running costs Cons Pressure required for gas supply Not suitable for washing semiconductors |
Advantages of our ultrafine bubble generator and the ultrafine pore method
Our proprietary world's only ultrafine bubble generator and the ultrafine pore method can gently generate bubbles with minimal energy consumption. Pressure of vapor phase that forms the bubbles, and differential pressure with the liquid phase: 0.1 Mpa Liquid phase flow to form bubbles: 1 m/sec Energy to dissolve the same amount of air into a liquid: 1/200 of normal aeration, 1/20 of swirl-type liquid flow method
The ultrafine bubble technology could potentially be used in a new type of medical treatment.
We have applied for a number of patents for this new product, which as many advantages over other similar products. Our technology will help create a society where people from all over the world can live together in mutual harmony and benefit the global environment. Together with researchers we aim to further develop new techniques and provide information on our other reliable technologies.
Various characteristics of ultrafine bubble
Recently, various characteristics of ultrafine bubble have been found.
During the concentration and collapse process ultrafine bubbles activate the oxygen in the air and form molecules, for example OH- and O3, with sterilization properties.
Ions present at the interface of ultrafine bubbles dissolve or absorb oil. This then enables cleaning without any use of detergents.
Ultrafine bubbles are present in every hole and corner of cells, and can thus improve immune systems. We have succeeded in reducing or complete eliminating the need for antibiotic drugs in some fish farms.
We confirmed that fish, crustacea, and plants developed with ultrafine bubbles grew 20 to 30% larger in size than normal.
We have confirmed that even when an oyster grown with ultrafine bubbles gets frozen at minus 20 degrees Celsius it is actually still alive. This is because the ultrafine bubbles protect the oyster from being damaged when frozen.
Heating ultrafine bubbles enables the liquid phase temperature to be increased faster. And contrary to this the liquid phase temperature can be very effectively decreased by decreasing the vapor phase temperature.
We confirmed that a liquid containing many ultrafine bubbles promotes its vaporization. This property can be used to improve the efficiency of water cooling towers and in vapor separation-based desalination devices.
Ultrafine bubble technology can be used to change the ecological balance of lakes, rivers, and the ocean, while also eliminating any bad odors and toxins resulting from anaerobic bacteria. Ultrafine bubbles can be distributed over wide areas, for example the ocean, and remain effective for a long period of time.


